Further reduced emissions
We have been reducing the use of coal and peat systematically. At the same time, our carbon dioxide emissions have reduced. We are also reducing our carbon dioxide emissions by improving energy efficiency. Sulphur dioxide and particle emissions have also decreased significantly.
A majority of our production companies have a certified ISO 14001-compliant environmental management system.
Our production companies Alholmens Kraft, Porin Prosessivoima (part of Pori Energy system), PVO-Vesivoima, Rauman Biovoima and Teollisuuden Voima have certified enervironmental management systems (ISO 14001). In addition, Kaukaan Voima and Kymin Voima have ISO 14001-compliant environmental systems that are not yet certified.
We have invested extensively in our thermal power plants to reduce emissions. The emissions of the plants depend on the fuels used, and on how much their annual production varies.
Pohjolan Voima’s thermal power plants use wood-based fuels such as by-products and residue from forestry, recycled fuels, peat, coal, and small amounts of natural gas and oil as start-up and backup fuels.
We are reducing the use of peat in a controlled manner. Read more on our climate work.
Already 99 % of our electricity generation is carbon neutral
We aim at 99% carbon-neutral electricity production and 85% carbon-neutral heat production in 2025. In 2024, already 99% of all electricity we produce was CO2 neutral. 89% of our heat production was carbon neutral.
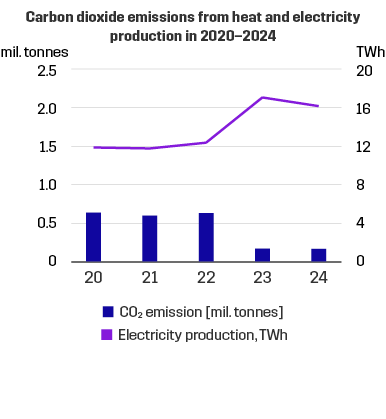
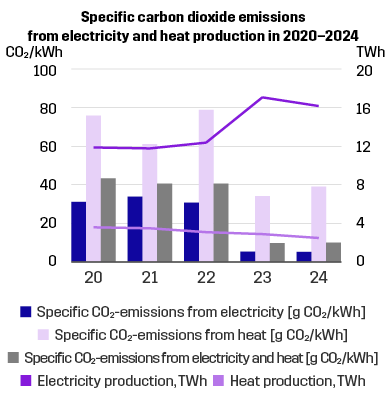
Our CO2 emissions have been decreasing mainly due to the fact that less coal – and peat – is used. In 2024 our
- carbon dioxide emission from the production of electricity and heat amounted to 0.2 million tonnes.
Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions
| 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| Scope 1 -GHG emissions | |||
| Gross Scope 1 GHG emissions (tCO2eq) | 276,685 | 157,740 | 136,901 |
| Percentage of Scope 1 GHG emissions from regulated emission trading schemes (%) | 91 | 85 | 87 |
| Scope 2 GHG emissions | |||
| Gross location-based Scope 2 GHG emissions (tCO2eq) | 2090 | 895 | 810 |
| Gross market-based Scope 2 GHG emissions (tCO2eq) | 5550 | 11,706 | 14,029 |
| Total GHG emissions | |||
| Total GHG emissions (location-based) (tCO2eq) | 278,774 | 158,635 | 137,710 |
| Total GHG emissions (market-based) (tCO2eq) | 282,235 | 169,446 | 150,929 |
| GHG intensity per net revenue | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Total GHG emissions (location-based) (Scope 1 and 2) per net revenue (tCO2eq/Monetary unit) | 852 | 603 | 579 |
| Total GHG emissions (market-based) (Scope 1 and 2) per net revenue (tCO2eq/Monetary unit) | 862 | 644 | 635 |
| Net revenue used to calculate GHG intensity (1000€) | 327,361 | 262,933 | 237,780 |
| Net revenue (other) (1000€) | 282,832 | 577,033 | 596,423 |
| Total net revenue (in financial statements) (1000€) | 610,193 | 839,964 | 834,203 |
| Wood-based biogenic CO2 emissions 2024 | 2024 |
| Wood-based biogenic CO2 emissions t/CO2 (Scope 1) | 1,152,300 |
Principles for the compilation of the metrics
Set in 2020, Pohjolan Voima’s carbon neutrality and peat reduction targets apply to the subsidiaries, associated companies and joint ventures. The figures are reported as consolidated figures. The figures of the subsidiaries are taken into account in the calculations with a 100% share. The figures for the associated company Alholmens Kraft and the joint venture Teollisuuden Voima are taken into account in the ratio of energy delivered to Pohjolan Voima.
The subsidiaries and the associated company Alholmens Kraft are taken into account in the indicator on the decrease in the use of peat as consolidated figures.
Teollisuuden Voima and Alholmens Kraft are not included in Pohjolan Voima’s Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions. Instead, they are included in Scope 3 emissions in category 1, Products and services delivered. The associated companies and joint ventures are not included in the fuel table or the calculation of wood-based biogenic carbon dioxide emissions either.
Pohjolan Voima has changed the consolidation calculation method for the 2024 figures. The figures for the previous years have been corrected to correspond to the new consolidation method.
Thermal power: focus on nitrogen oxides
In recent years, we have worked hard to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions. Development work on this has been underway in all of our combined heat and power production plants. An example of this is development of boiler control. With the technology supplier Valmet, we have developed control technology for the boiler of the power plant so that we can control the combustion process more efficiently. This minimises the generation of nitrogen oxides.
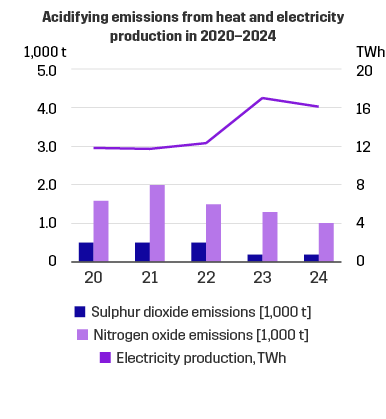
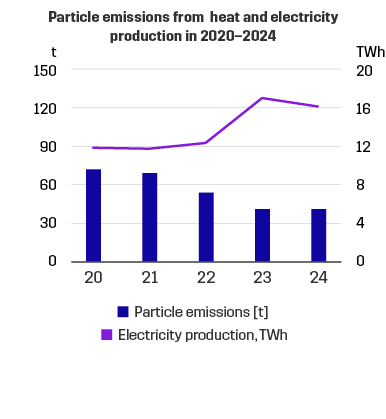
In 2024, our emissions to the air amounted to:
- sulphur dioxide emissions amounted to 0.2 tonnes
- nitrogen oxide emissions to 1.0 thousand tonnes
- particle emissions to 0.05 tonnes.
See more: emission figures
See also more on emissions in our Annual Report 2024.
The emissions of each of our thermal power plants are presented on their respective pages, see more at Power plants -pages.
Precise control of the combustion process
In thermal power plants, precise control of the combustion processes in the boilers improves energy efficiency and reduces emissions. State-of-the-art sampling technology in the smokestacks of the power plants produces constant information about emissions.
For example, Rauman Biovoima uses sampling technology, which provides precise real-time data on the concentrations of about 20 compounds.
Hydropower: CO2-neutral electricity
The production of hydropower does not cause CO2 emissions into water or the ground. Nor does it generate solid waste. In Finnish latitudes and in the northern climate, methane emissions are estimated to remain low. This situation is very different in subtropical and tropical regions, where methane emissions in water reservoirs have been studied most.
Methane is generated when organic material decomposes in reservoirs. Generally, Finnish power plants use natural waterways to produce hydropower, which reduces emissions.
The energy efficiency of hydropower plants has been and will be improved at regular intervals. This further reduces emissions per energy unit produced. Renovations also bring environmental benefits. For example, the risk for oil leaks has been minimised when water has replaced oil as lubricant in turbines.
Nuclear power: a key role in climate work
Nuclear power is a zero-emission form of electricity production. It plays a very significant role in climate work in Finland and the EU. In Europe, nuclear energy is used in about half of all low-emission electricity production. In Finland, nuclear power, along with hydropower, is the most important source of low-emission electricity.
For more information about the environmental issues of nuclear power and the final disposal of spent nuclear fuel, for example, please visit the website of TVO and Posiva.